Future Value FV of a Single Amount: Definition, Formula, and How to Calculate It
The PV calculation takes into account the time value of money, or the idea that a rupee today is worth more than a rupee tomorrow. This is due to the fact that money can be invested and earn interest over time. The discount rate is highly subjective because it’s the rate of return you might expect to receive if you invested today’s dollars for a period of time, which can only be estimated.
Table of Contents

For example, if the interest rate earned is 6%, it will take 12 years (72 divided by 6) for your money to double. If you want your money to double every 8 years, you will need to earn an http://taihengfurniture.com/working-capital-ratio-meaning-formula-components/ interest rate of 9% (72 divided by 8). The Rule of 72 indicates than an investment earning 9% per year compounded annually will double in 8 years.

Example 1 – Calculate the Present Value for a Single Payment
The answer tells us that receiving $10,000 five years gym bookkeeping from today is the equivalent of receiving $7,440.90 today, if the time value of money has an annual rate of 6% compounded semiannually. We need to calculate the present value (the value at time period 0) of receiving a single amount of $1,000 in 20 years. The interest rate for discounting the future amount is estimated at 10% per year compounded annually.
Present Value Equation
- The future value of multiple amounts is determined by calculating, and then adding together, the future value for each single amount.
- Calculating the present value (PV) is a matter of plugging FV, the interest rate, and the number of periods into an equation.
- It sure would help if they know how much the $100,000 would grow if they invested it.
- The present value of a single sum tells us how much an amount to be transacted in the future is worth today.
- Calculations #9 through #12 illustrate how to determine the interest rate (i).
Because the PV of 1 table had the factors rounded to three decimal places, the answer ($85.70) differs slightly from the amount calculated using the PV formula ($85.73). We’ll discuss PV calculations that solve for the present value, the implicit interest rate, and/or the length of time between the present and future amounts. If you are scheduled to receive $10,000 one year from today, what is its value today, assuming a 5.5% annual discount rate? The “annual discount rate” is the rate of return that you expect to earn on your investments. There is no single “correct” answer, but you should use a realistic number based on your own investment history. This is equivalent to saying that at a 12% interest rate, compounded annually, it does not matter whether you receive $8,511.41 today or $15,000 at the end of five years.

- Similarly, the interest rate is converted from 10% per year to 5% per semiannual period.
- Before you dive into annuities, IRRs, or discounted cash flow models, you must understand how to move a single lump sum backward or forward in time.
- Of course, both calculations could be proved wrong if you choose the wrong estimate for your rate of return.
- Our focus will be on single amounts that are received or paid in the future.
- A balance on the right side (credit side) of an account in the general ledger.
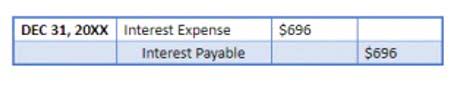
- The interest for the third quarter is $208 ($10,404 x 2%) and the interest for the fourth quarter is $212 ($10,612 x 2%).
- Understanding the future value of a single amount is the foundation for the more complex future value.
The present value is computed either for a single payment or a series of payments to be received in future. This article explains the computation of present value of a single payment to be received at a single point of time present value of a single amount in future. To understand the computation of present value of a series of payments to be received in future, read present value of an annuity article. Present value is a way of representing the current value of a future sum of money or future cash flows. The higher the discount rate you select, the lower the present value will be because you are assuming that you would be able to earn a higher return on the money. Present value (PV) is based on the concept that a sum of money in hand today is probably worth more than the same sum in the future because it can be invested and earn a return in the meantime.
- Suppose that a company with an extra $100,000 lying around is trying to decide between investing the money at 4 percent for five years and using the extra money to expand the business.
- The Rule of 72 indicates than an investment earning 9% per year compounded annually will double in 8 years.
- It means if the amount of $3,415 is invested today @10% per year compounded annually, it will grow to $5,000 in 4 years.
- It is also a good tool for choosing among potential investments, especially if they are expected to pay off at different times in the future.
- Except for minor differences due to rounding, answers to equations below will be the same whether they are computed using a financial calculator, computer software, PV tables, or the formulas.

